An Empirical Study of LLaMA3 Quantization From LLMs to MLLMs
Specifically, we comprehensively evaluate the 10 existing post-training quantization and LoRA-finetuning methods of LLaMA3 on 1-8 bits and diverse datasets to reveal LLaMA3’s low-bit quantization performance.
Our findings indicate that while LLaMA3 still demonstrates superior performance after quantization, the performance degradation associated with quantization is significant and can lead to larger declines. This drop is mainly because the powerful pre-training process enables LLaMA3 to learn more information on a similar scale compared to the previous LLaMA and LLaMA2.
Our study delineates the outcomes of two principal techniques (PTQ, LoRA-FT) for quantizing LLaMA3 across three evaluation tracks
- Post-Training Quantization (PTQ)
- Quantization of LLMs via LoRA-FineTuning (LoRA-FT)
- PTQ of LLaMA3-based MLLM
cutting-edge quantization methods
RTN (vanilla)
GPTQ (efficient and effective)
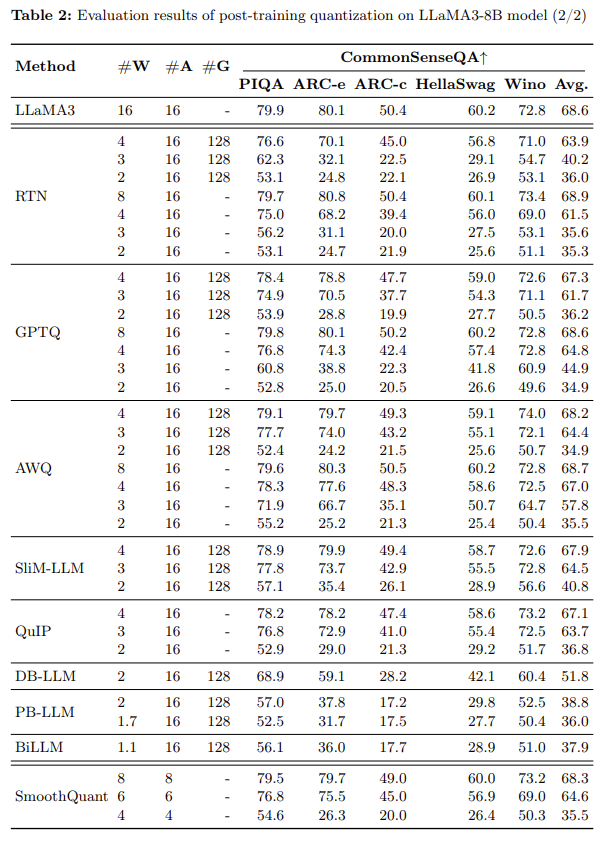
GPTQ [6] is currently one of the most efficient and effective weight-only quantization methods, which utilizes error compensation in quantization. But under 2-3 bits, GPTQ causes severe accuracy collapse when quantized LLaMA3.
AWQ
AWQ [12] adopts an anomaly channel suppression approach to reduce the difficulty of weight quantization
SmoothQuant
PB-LLM
QuIP
DB-LLM
BiLLM
SliM-LLM for PTQ
QLoRA
IR-QLoRA for LoRA-FT
For multimodal tasks, we follow a common practice [12], performing lowbit post-training quantization on the LLM component of LLaVA-Next-8B using GPTQ and AWQ.